How does Document AI work

Enterprises generally deal with large amount of documents generated from variety of sources on which they have no control. And they end up with large amount of data which they need to process for business continuity or compliance reasons.
Google cloud and many other startups have document AI service, where upon processing the document, they will output
- Key value pairs pertinent to the document e.g. first name, last name (ID card), bill amount, address (invoice) etc.
- Identify tables and extract values to be processed later on.
- extract text using OCR techniques. Today we will take a look at what is going on behind this end to end service.
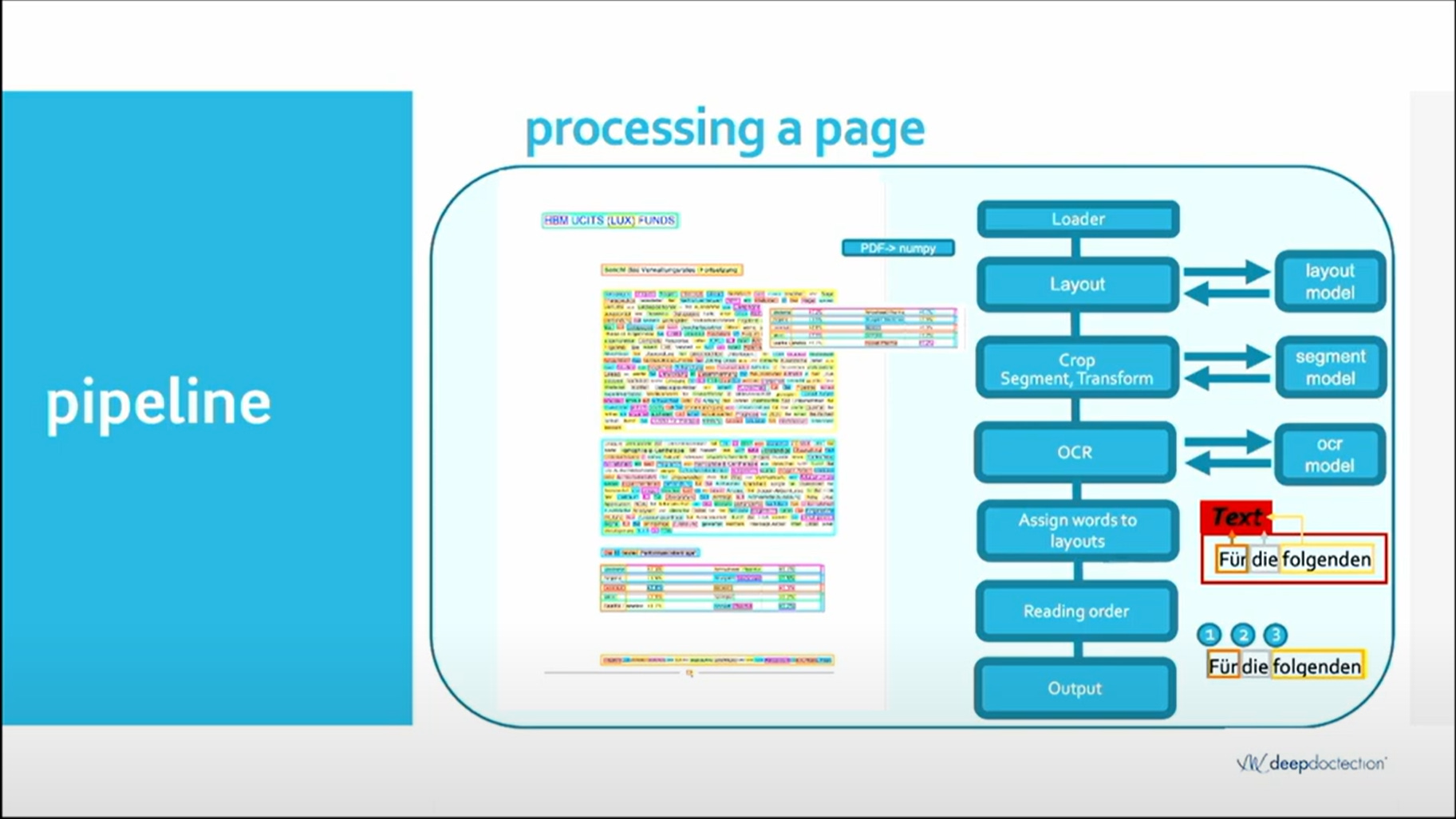
In the diagram below, you can see several stage a document goes through before outputting the extracted metadata.
- A load will load the document and extract legible text wherever it can.
- Layout detector segment and detect different layouts e.g. table, paragraph, form with key value pairs, signatures, invoices etc.
- OCR model will run OCR to extract the text for segments
- Table detection, extraction, structure recognition. This will idenity table area, highlight columns, different cells and expanded cells, along with headers. From these it will extract values and link them together.
- Document question answering model will answer questions given a document.
Most of these models are available on huggingface along with some open data to try the model on. In addition to cloud providers and VC-funded startups, an open-source project deepdoctection has put together all these models and tools together to create a toolbox for anyone to build and tune a document processing pipeline.
As this model will need finetuning invariably, a need for labelling tool emerges. There are no good open-source labelling tools as of today, says the author of deepdoctection.
There are good commercial labelling tools such has labelbox and Scale AI which offers one-stop annotation tools designed for labelling

- Image - bounding box for object detection, mask overlay for instance segmentation, keypoint detection for pose/gesture estimation, classification
- Text: POS and NER tagging. text classification, translations.
- Video: action detection,
- music: tagging
- Documents: Table detection and extraction, layout detection, digitization.
Most of these tools run ML models to generate label proposals which are reviewed by a human before they are accepted as training data for labels. These labels are not only essential for training ML models, but also for fine-tuning models. So far big tech companies have been using these tools to generate high-quality training data, but soon smaller shops will also need it for fine-tuning the base models for their use cases.